To meet the automotive industry’s goal of achieving high-strength, lightweight body structures to achieve 5-star crash performance, automakers plan to further increase their use of high-strength advanced high-strength steel/ultra-high-strength steel. Electric vehicles, in particular, will need to use stronger materials in new ways, especially to carry and protect their heavy battery packs.
For many years, 1.5 GPa steel has been roll formed to create relatively simple profiles for automotive body-in-white applications. But now, systematic advances in stamping technology offer body-in-white designers and production engineers the opportunity to cold stamp 1.5 GPa steel for moderately complex contours, rather than relying solely on hot forming.
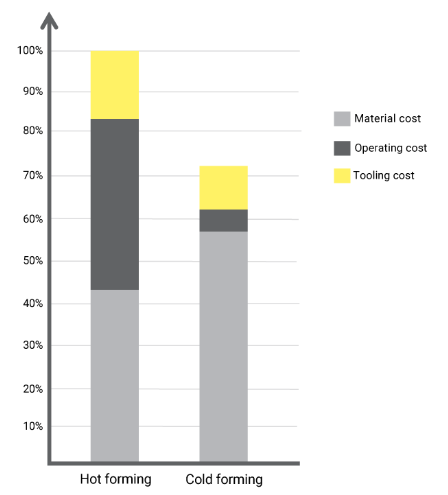
Advantages of Cold Forming in GigaPa Steel:
- Cost reduction of 28%: Since the operating costs of hot stamping are significantly higher, the cold forming process is much less expensive than hot forming.
- Compared with hot stamping, energy consumption is significantly reduced, thus reducing energy costs and CO2 emissions.
- Compared to hot formed steels (PHS), martensitic steels have a wider range of mechanical properties.
- The final surface quality of cold formed martensitic parts is better than that of hot stamped parts.
- Cold stamped parts require no additional cleaning (shot blasting).
- Cold-stamped parts can be mechanically punched and trimmed, while hot-formed parts require a more expensive laser cutting operation to avoid hydrogen embrittlement.
- The zinc coating on martensitic steel provides cathodic corrosion protection.
- Martensitic steels have better welding properties than PHS due to their lower carbon equivalent (Ceq or C.E.).