High plasticity dual phase steel – CR850/1180DH
What are the microstructure characteristics of high plasticity dual phase steel?
High ductility dual phase steel is a specially engineered steel for excellent formability and high strength. The microstructure of such steels is usually characterized by two main phases:
Ferrite: This phase consists of iron with small amounts of carbon and other alloying elements. It has a body-centered cubic (BCC) crystal structure and is relatively soft and malleable.
Martensite: This phase is formed by transforming part of the ferrite phase through a process called quenching and tempering. It has a body-centered tetragonal (BCT) crystal structure and is very hard.
The microstructure of high ductility dual-phase steels usually consists of a mixture of these two phases, with the ferrite phase as the soft matrix and the martensite phase as the reinforcing phase. This unique microstructure makes steel both strong and ductile, with excellent formability and the ability to resist deformation without cracking or breaking.
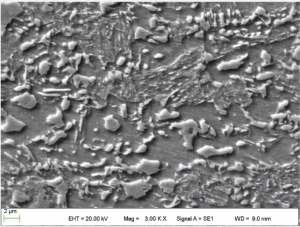
Typical metallographic structure of high ductility dual phase steel
What are the performance characteristics of high plasticity dual phase steel?
High ductility dual phase steel is an advanced high strength steel designed with superior performance characteristics compared to conventional steels. Some key performance characteristics of high ductility dual phase steels include:
Through the TRIP effect of retained austenite in the microstructure sink during deformation, DH steel has better drawing formability and impact energy absorption than DP steel, and high plasticity dual-phase steel also has lower LME sensitivity.
What kind of steel is CR850/1180DH?
CR850/1180DH is a high ductility dual phase steel. It is a member of the high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steel family, specifically designed to exhibit high strength and excellent ductility. The designation “CR850/1180DH” refers to the minimum yield strength (850 MPa) and tensile strength (1180 MPa) of the steel.
The microstructure of CR850/1180DH steel generally consists of a soft ferrite matrix with islands of hard martensite dispersed throughout the structure. This unique microstructure gives the steel high strength and excellent ductility, making it ideal for applications where both strength and formability are important, such as the automotive and aerospace industries.
In addition to high ductility and strength, CR850/1180DH steel has good weldability and can be easily welded using standard welding techniques. Overall, CR850/1180DH is an attractive material for a wide range of industrial applications requiring high strength and excellent ductility.
What are the characteristics of CR850/1180DH steel?
CR850/1180DH steel is a high strength steel that has been engineered for high strength and excellent ductility. Some of the key properties of CR850/1180DH steel include:
High Strength: With a minimum yield strength of 850 MPa and a minimum tensile strength of 1180 MPa, CR850/1180DH steel is a very strong material.
High Ductility: The soft ferrite matrix and islands of hard martensite dispersed in the microstructure of CR850/1180DH steel give it excellent ductility, meaning it can withstand large deformations without cracking or fracturing.
Good Formability: The high ductility of CR850/1180DH steel allows it to be easily formed into complex shapes without cracking or tearing, making it an ideal material for use in applications where formability is important.
Excellent weldability: CR850/1180DH steel has good weldability, which means it can be easily welded using standard welding techniques.
Lightweight: CR850/1180DH steel is a lightweight material ideal for use in applications where weight reduction is important, such as the automotive and aerospace industries.
Improved crashworthiness: The high energy absorption capacity of CR850/1180DH steel makes it an excellent material for automotive crash structures, helping to improve passenger safety.
Overall, the combination of high strength, excellent ductility, good formability and excellent weldability make CR850/1180DH steel an attractive material for a wide range of industrial applications where both strength and formability are required.

What is the chemical composition of CR850/1180DH steel?
CR850/1180DH steel is a high strength low alloy (HSLA) steel generally composed of the following chemical elements:
Carbon (C): 0.14% – 0.18%
Silicon (Si): 0.15% – 0.40%
Manganese (Mn): 1.00% – 1.50%
Phosphorus (P): ≤0.020%
Sulfur (S): ≤0.015%
Chromium (Cr): ≤0.30%
Nickel (Ni): ≤0.30%
Copper (Cu): ≤0.30%
Molybdenum (Mo): ≤0.10%
Aluminum (Al): ≥0.015%
Titanium (Ti): ≤0.15%
The exact chemical composition of CR850/1180DH steel may vary depending on the manufacturer and the specific application of the steel. However, in general, CR850/1180DH steels are designed with a low carbon content and a high content of alloying elements, which contribute to their strength and ductility.
What are the mechanical properties of CR850/1180DH steel?
CR850/1180DH steel is a high strength low alloy (HSLA) steel with excellent mechanical properties including high strength, high ductility and good formability. The following are typical mechanical properties of CR850/1180DH steel:
Yield strength: 850 MPa (minimum)
Tensile strength: 1180 MPa (minimum)
Elongation: 12% (minimum)
Area reduction: 50% (minimum)
Hardness: 250-320 HB
These mechanical properties make CR850/1180DH steel an attractive material for a wide range of industrial applications, including automotive and aerospace structures, where both strength and formability are important. The high strength of CR850/1180DH steel enables it to withstand high stress without deformation, while its excellent ductility and formability allow it to be easily formed into complex shapes without cracking or tearing. In addition, CR850/1180DH steel has good weldability and can be easily joined to other components using standard welding techniques.
What is the manufacturing process of CR850/1180DH steel?
CR850/1180DH steel is typically produced using a process known as dual phase (DP) steel processing. The DP steel manufacturing process involves several steps, including:
Hot rolling: Steel is first heated to high temperatures and then passed through a series of hot rolling mills to reduce its thickness and shape it into long, flat strips.
Cold rolling: The hot rolled strip is then cooled and passed through a series of cold rolling mills to further reduce its thickness and improve its surface finish.
Annealing: put the cold-rolled steel strip into the furnace for high-temperature annealing to soften the steel and prepare for the next step of processing.
Quenching: The annealed steel strip is rapidly cooled by a water bath or other cooling medium, so that the steel undergoes a phase transformation from austenite to martensite.
Tempering: The quenched strip is then tempered in a furnace at a lower temperature to reduce its hardness and increase its ductility.
Cutting and Forming: The tempered steel strip is then cut and formed into the desired shape using standard metalworking techniques.
The resulting CR850/1180DH steel has a unique microstructure consisting of a soft ferrite matrix and islands of hard martensite dispersed throughout the structure. This microstructure gives CR850/1180DH steel excellent strength and ductility, making it an ideal material for a wide range of industrial applications.
What are the uses of CR850/1180DH steel in automobile manufacturing?
CR850/1180DH steel has become a popular material in the field of automobile manufacturing due to its high strength, good ductility, and good formability. Some common uses of CR850/1180DH steel in automotive manufacturing include:
Body structure: CR850/1180DH steel is often used in the manufacture of automobile body structures, including frame, roof, columns, etc. The high strength of CR850/1180DH steel enables it to withstand high stress and impact, while its excellent ductility and formability allow it to be easily formed into complex shapes and integrated with other components.
Suspension Components: CR850/1180DH steel is also used in the manufacture of suspension components such as control arms, springs and struts. The high strength and ductility of CR850/1180DH steel make it an ideal material for these components that must be able to withstand high loads and repeated impacts.
Exhaust systems: CR850/1180DH steel is commonly used in the manufacture of exhaust systems including pipes, mufflers and catalytic converters. The high strength and heat resistance of CR850/1180DH steel make it an ideal material for these components that must be able to withstand high temperatures and corrosive environments.
Safety components: CR850/1180DH steel is also used in the manufacture of various safety components such as seat frames, seat belts and airbag components. The high strength and ductility of CR850/1180DH steel make it an ideal material for these components, which must withstand the high stresses and impacts experienced during a crash.

Application case of CR850/1180DH steel – front longitudinal beam inner panel
What are the supply standards for high plasticity dual phase steel?
High ductility dual phase (DP) steels are supplied according to various international and industry standards which specify the chemical composition, mechanical properties and other quality requirements of the steel. Some common supply standards for high ductility DP steels include:
| Steel Grade | Yield Strength(MPa) | tensile strength(MPa) | EL% |
| CR550/980DH | 550-700 | 980 | 15 |
| CR700/980DH | 700-850 | 980 | 14 |
| CR850/1180DH | 850-1050 | 1180 | 13 |
a .lf the yield point is not pronounced, the values of Rpo., apply. Otherwise, the values of Reapply.
- Guaranteed for No.5 tensile specimens according to standardJISZ2241 with the tensile axis parallel to the rolling direction Note: Please confrm the specifications of product before official order. The specifications are negotiable.

