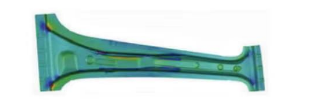
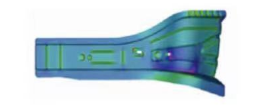
Hot stamping is a forming process in which a metal material is heated to a high temperature state, and then a high pressure is applied in a mold to cause plastic deformation and form a desired shape. Hot stamping is usually used to produce complex and precise parts and products, which can be formed under unidirectional or multi-directional pressure, and can take advantage of the high-temperature softening properties of metal materials to achieve more precise forming.
In the hot stamping process, the metal material first needs to be heated to a specified temperature range to reduce the flow resistance of the material and increase its plasticity. Next, the preheated metal material is placed into a mold, and then subjected to high pressure to plastically deform it in the mold to finally form a part or product in the desired shape. Hot stamping can use various types of molds, including one-way molds, multi-directional molds and composite molds, etc., to meet the needs of different shapes and sizes.
Compared with traditional mechanical processing methods, hot stamping has many advantages, such as high forming precision, good surface finish, and no need for subsequent processing, so it is widely used in automobiles, aviation, electronics, instrumentation and other fields.
Process of hot stamping
Hot stamping is a forming process in which metal materials are heated to a high temperature state, and then high pressure is applied in a mold to cause plastic deformation and form the desired shape. The following is the basic process of hot stamping forming:
Material preparation: choose the appropriate metal material, heat the material and reserve margin and other preparatory work.
Mold design and manufacture: According to the design requirements of parts or products, design and manufacture suitable molds, and conduct mold trial debugging.
Heating and pasting: put the metal material into the heating furnace for heat treatment, make it reach the specified molding temperature, and then place and paste in the mold.
Forming: applying high pressure to cause plastic deformation of the metal material in the mold, forming the required part or product shape according to the design requirements.
Cooling and taking out: After the part or product is formed, stop heating and cool in the mold for a period of time, then take out the formed part or product.
Subsequent processing: discharge, clean, polish, descale and other subsequent processing of the formed parts or products to make them meet the final design requirements.
The above is the basic process of hot stamping, and the specific process and steps may vary with different products or materials.
Application fields of hot stamping
The hot stamping forming process has the advantages of high forming precision, good surface finish, and no need for subsequent processing, so it is widely used in the following fields:
Automobile manufacturing: hot stamping can be used in the manufacture of automobile chassis, body, engine and its parts.
Aerospace: Hot stamping can be used to manufacture aircraft structural parts, missile structural parts, satellite structural parts, etc. in the aerospace field.
Electronic devices: Hot stamping can be used to produce casings and components of electronic products such as mobile phones, tablets, and laptops.
Instrumentation: Hot stamping can be used to produce shells and parts of various instruments.
Precision machinery: hot stamping can be used to produce various precision machinery parts.
Building decoration: hot stamping can be used to produce building materials such as building doors and windows, curtain walls, aluminum plates, etc.
In general, hot stamping is widely used in various fields, capable of manufacturing high-quality, high-precision parts and products, improving production efficiency, reducing costs, and promoting the development of modern industry.
Advantages of hot stamping
Hot stamping is a popular manufacturing process that offers many advantages over other metal forming techniques.
First, hot stamping allows the production of complex and high-strength components with excellent dimensional accuracy. This is due to the use of heated tools, which allow precise shaping and deformation of the material even when it is in its hardened state.
Second, hot stamping offers superior material utilization by reducing scrap rates during production. This reduces material costs compared to traditional forging or casting methods.
Third, parts produced by hot stamping have higher fatigue resistance, ductility, and toughness than conventional cold forming processes. In addition, the resulting parts have better corrosion resistance due to their uniform microstructure.
Hot stamped parts typically require fewer secondary operations, such as machining or welding, as they can be integrated directly into components without additional processing steps. This reduces lead times and overall costs while improving product quality.
These advantages make hot stamping an attractive option for many industries that require high-performance lightweight structures with minimal waste generation.
in conclusion
All in all, hot stamping is an efficient and cost-effective manufacturing process that offers many advantages over other forming methods. Its ability to produce lightweight yet strong parts with high dimensional accuracy makes it ideal for a variety of industries including automotive, aerospace and consumer goods.

